Contextualizing UNESCO’s Historic Urban Landscape Approach: A Framework for Identifying Modern Heritage in Post-Blast Beirut
Abstract:
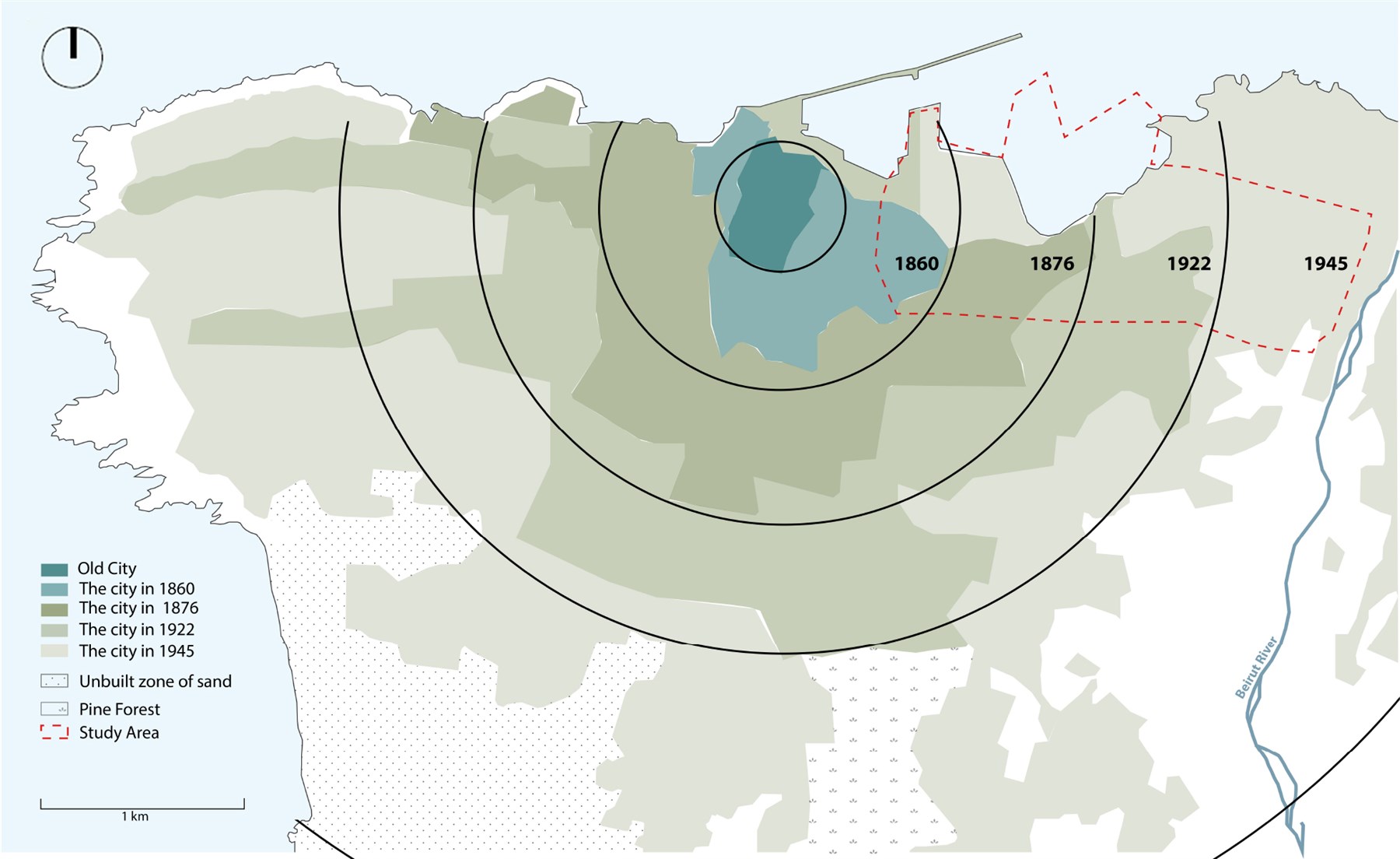
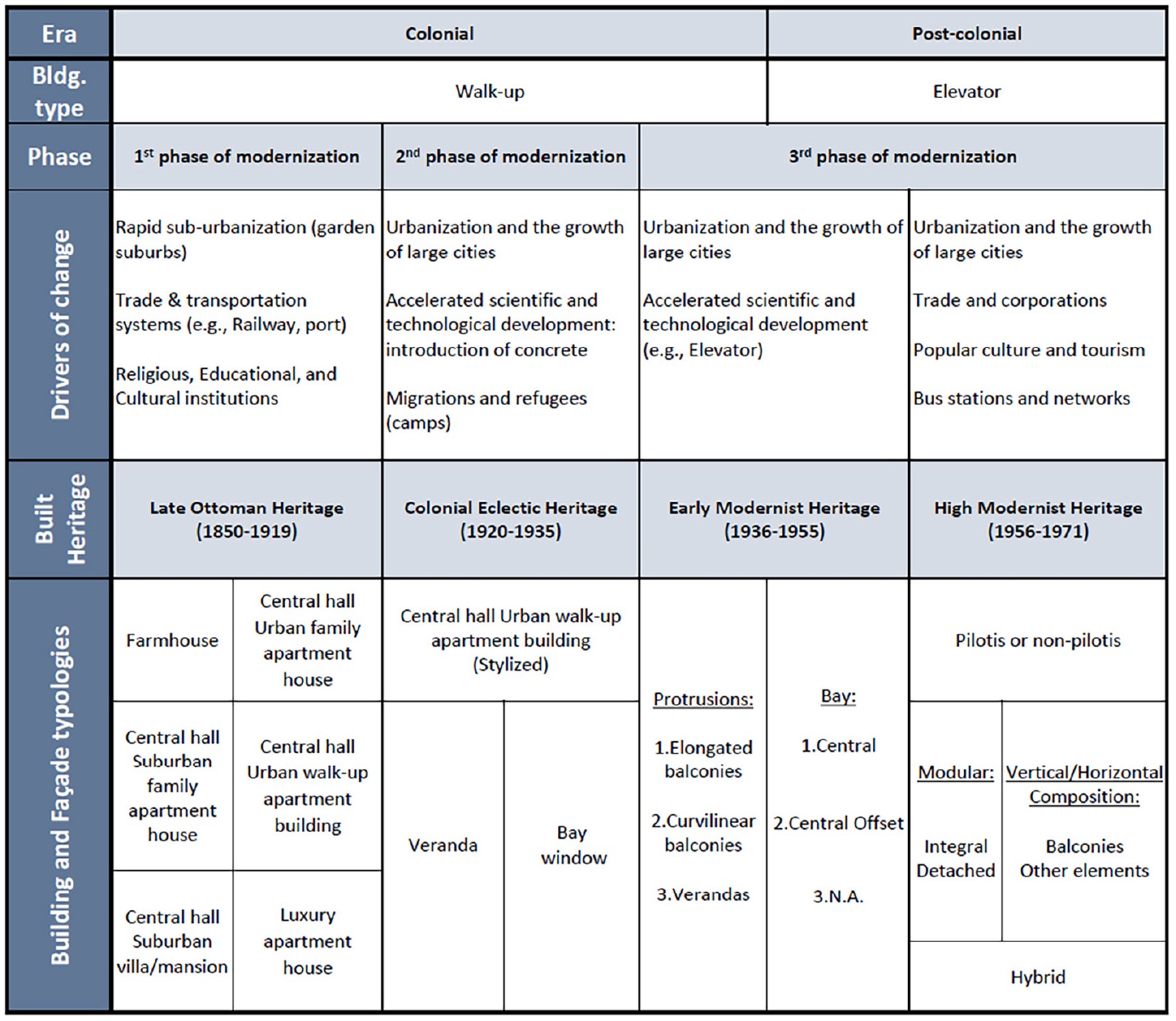
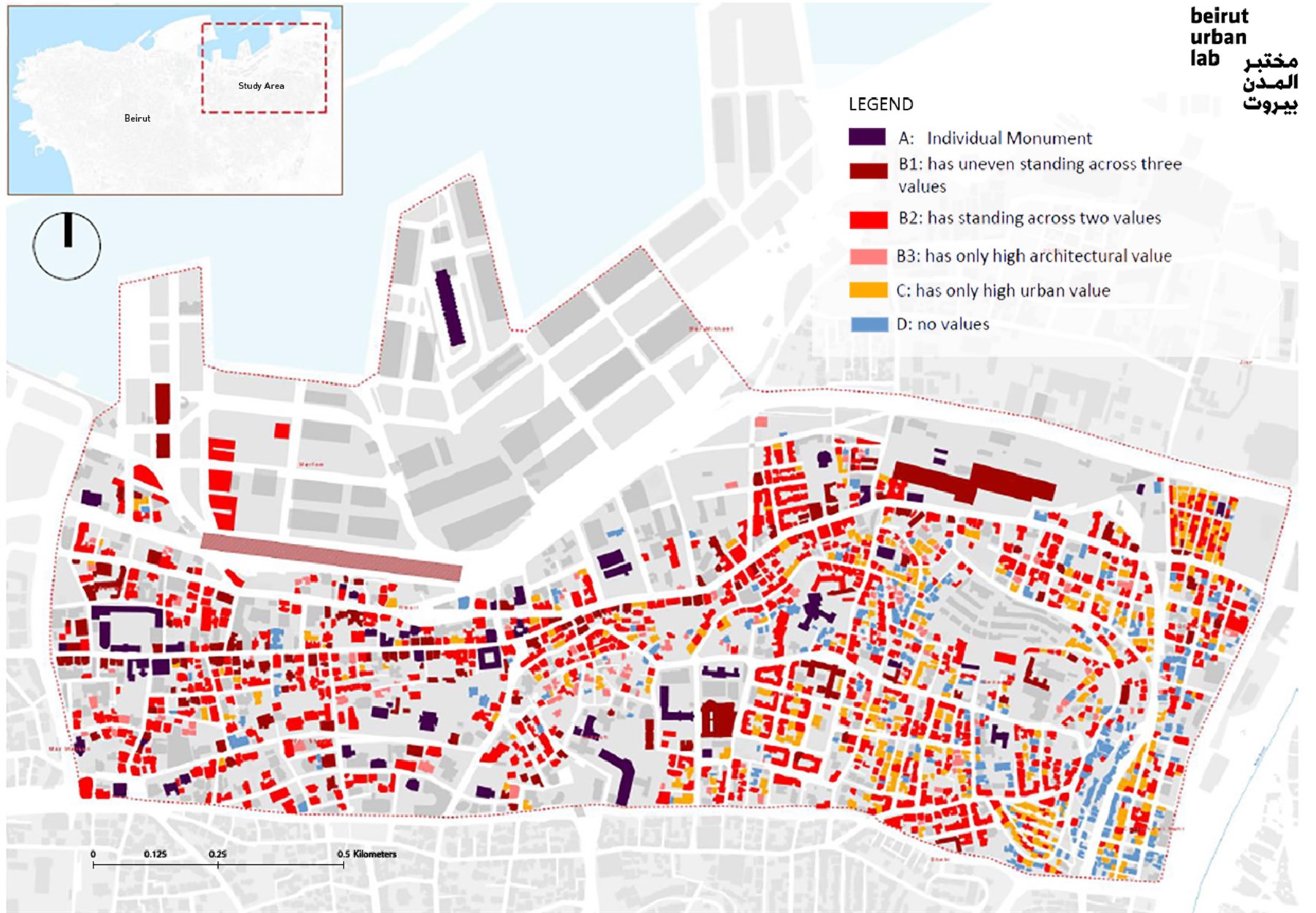
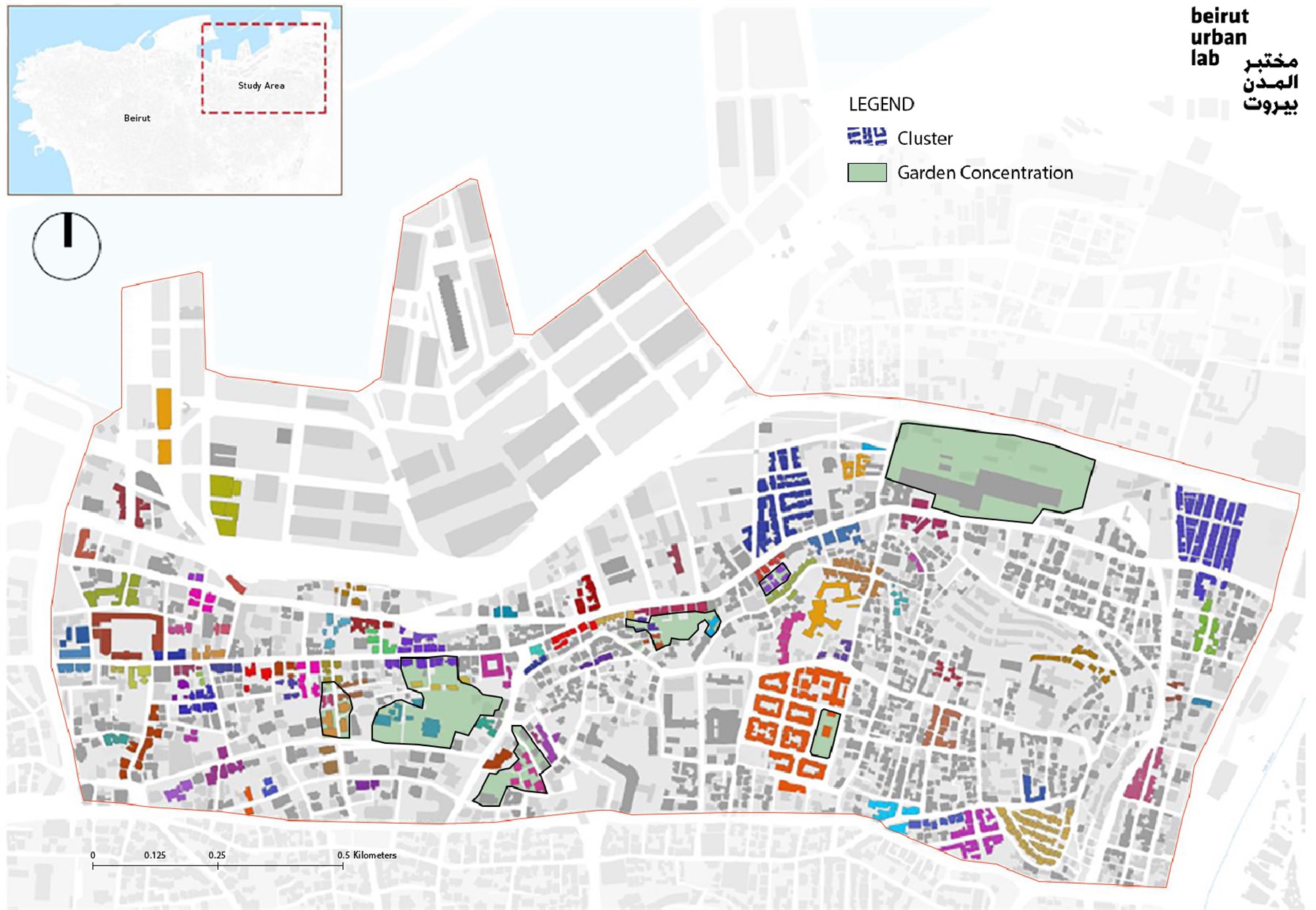
This paper reflects on the application and adaptation of the Historic Urban Landscape (HUL) approach in Beirut, Lebanon, in post-disaster conditions. Adopted by UNESCO in 2005, the HUL approach marked a shift in addressing urban heritage, echoing an evolution in theory. However, contextualizing the HUL approach to address distinct local, geographic, and cultural conditions and reframing its scale and scope of operation remains a challenge. This paper uses a case-study-based methodology as it reflects on the application of the Historic Urban Landscape approach in the post-blast context of Beirut. Commissioned by UNESCO, an interdisciplinary team at the Beirut Urban Lab used the HUL approach to identify modern heritage in Beirut after adapting it to the post-colonial and Mediterranean context of the city. This study contextualized modern heritage definitions, proposed a periodization of modern built and landscape heritage, and designated modern heritage based on its formal/spatial, urban/landscape, socio-cultural, and environmental values. This paper argues that the study contributes to the advancement of the Historic Urban Landscape approach by operationalizing it into an applicable heritage framework, employing a transdisciplinary model that involves local people at the institutional and community levels, and serving as a basis for generating conservation strategies responsive to place and culture. This study also pioneered a comprehensive, integrative, and transdisciplinary reading of modern heritage in Beirut, breaking the professional silos between disciplines and bringing landscape into the identification of heritage in Lebanon.
Read the full paper on the MDPI website.