To Pre-empt Disaster Capitalism, Beirut Urgently Needs a People-centered Recovery
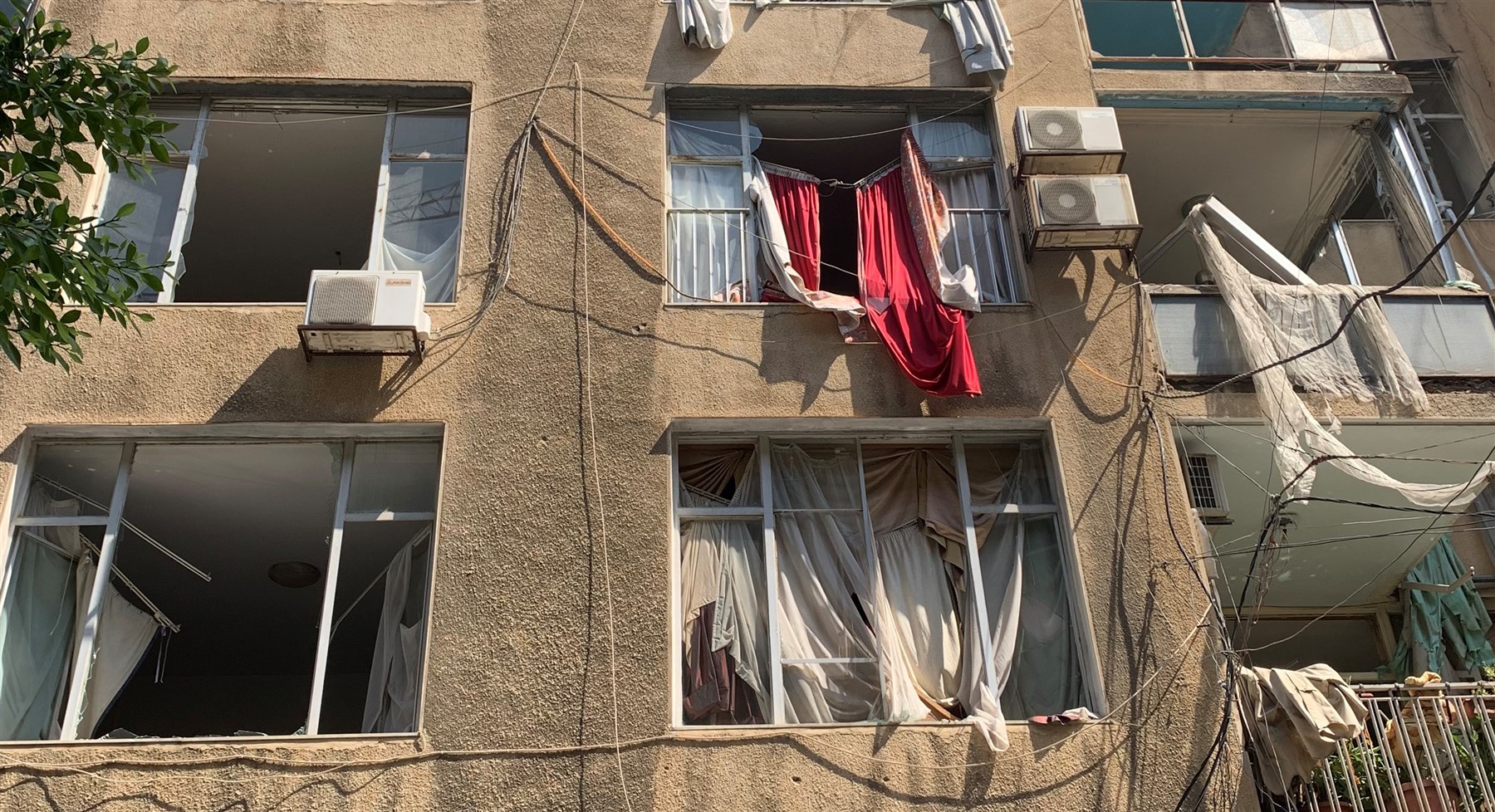

Electricity and water are cut off in many areas, while threats of structural failure –sometimes bolstered by assessments that err on the side of “safety”- precipitate the departure of a traumatized population. Tens of buildings are factually inhabitable, their doors and windows having blown out. Others are too close to the devastation zone to feel safe. Meanwhile, food tents set up to respond to emergency needs have consolidated the districts as “sites of humanitarian response,” attracting other poor populations who have flocked from other sectors of the city to benefit from direly needed food relief. As the army takes over the districts this evening, an eerie sentiment of danger invades souls. Looking forward, the emergency is for restoring any element of normalcy in the districts and empowering neighborhood dwellers’ return. This will be imperative for the city to reignite life and avoid seeing more of its quarters hijacked by real estate interests, as feared by many of the residents I was able to talk to. Residents’ angsts are fueled by disaster scenarios that would replicate earlier experiences of post-war reconstruction in Lebanon, particularly the experience of the real-estate company Solidere in Beirut’s historic core at the end of the civil war (1990). Not only did the real-estate company prevent permanently long-term stakeholders’ return, but two decades later, there are ample proofs that despite generous public subsidies and facilities, it has failed to recover the city’s heart or generate an urban life or a functional economy to animate it. Rather than reversing the effects of the war, the post-civil war intervention in Downtown Beirut effectively consolidated the effects of the violence of the war. We should not repeat this mistake. The departure of so many residents and businesses in the districts surrounding the port, even when the buildings that hosted them are repairable, will pose a serious threat to the recovery of the city and its districts. To be sure, there are challenges to a rapid rehabilitation when most residents and business owners are impoverished by months of lock-down overlapping with a global economic crisis and an unprecedented national financial melt-down. But to properly assess the danger of this rapid evacuation turning into a permanent displacement, one needs to locate the effects of the blast within the recent histories and trajectories of the neighborhoods surrounding the port. The historical districts surrounding the port, namely Mar Mikhael, Gemmayzeh, and Geitawi, had been subjected to the ravaging forces of unbridled financial capital for at least a decade.1 Propelled by aggressive speculative property investments in a context of a failing national currency, the neighborhood was already seeing its long term residents evacuated. In the areas falling within the delineated perimeter of severe damage highlighted by the National Higher Relief Commission, the Beirut Urban Lab’s survey of Beirut in 2018 counted more than 250 empty lots –many the location of demolished buildings- and another 120 fully evacuated buildings, sold to developers who were waiting for the appropriate moment to bring them down. At least 350 demolition permits had also been filed within the same district over the past 15 years. In total, these evicted sites account for almost 1 in 9 buildings in the area!2 As the research team’s findings indicate, these investments were the outcome of overlapping public policies that incentivized the flow of financial capital in the built environment through series of exemptions and incentives to financial institutions. Halted for a couple of years as the real estate market seemed to slow down, the trend had been energized by the financial meltdown as account holders rushed to find safer destinations to store their money once the banks proved unsolvable and unreliable.
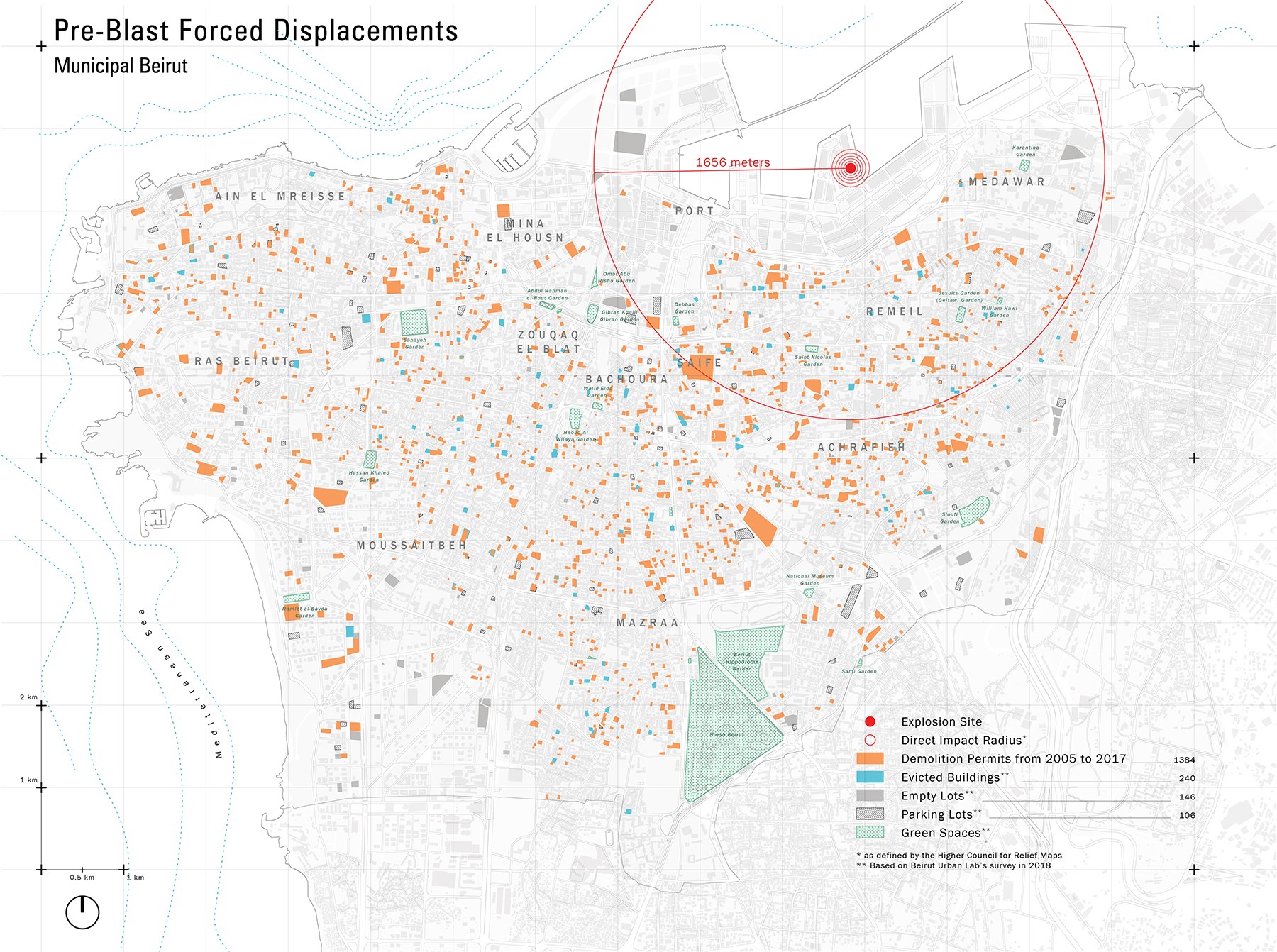
In addition, the inadequacy of housing policies had rendered the conditions of many middle and lower income residents untenable for many years. Thus, unregulated rental agreements pitted landlords against tenants, particularly after the unofficial devaluation of the Lebanese pound drove rental costs through the roof, pitting tenants and property owners against each other in draining negotiations. Similarly, the inability to resolve the suspended rent control regulations appropriately encouraged landlords whose properties have been held under a severely skewed rent control for fifty years to sell their properties at any cost. Moreover, poor urban regulations left the neighborhood in uncomfortable cohabitations of populations with divergent aspirations, such as bar goers and elderly residents who fought each other with statements, legal complaints, and everyday forms of resistance (e.g., insults, water buckets) in the absence of a strong regulator. More generally, neglect of public infrastructure with water and sewer networks often dating back to the 1940s had left some of the neighborhoods in poor conditions, driving away those who could afford it. These factors, and others, had already pushed many property owners to sell their homes and lands. In the aftermath of the blast, many rumors circulate about developers and realtors already approaching residents to incentivize them to leave. The danger is real. In the absence of effective public agencies and a well-coordinated state effort, trust in post-disaster recovery needs to be invested in people. The residents of the neighborhoods, their business owners, workers –including school teachers, hospital staff, etc.- and visitors should be empowered to restore life in homes and workspaces. True, attention needs to be paid for the specific architectural value of some of the buildings and their unique construction techniques, as well as the structural safety of the most-affected buildings. While I am sympathetic to the imperative of preserving historical buildings, the efforts of preservation and safety need to work with the residents, bringing them on board, and prioritizing the lifelines that will make it possible for them to return. Thus, legal barriers (e.g., permitting, property considerations) need to be lifted immediately, and the tendency to develop “future plans” and freeze areas under study needs to be resisted. Instead, incentives need to be put forward for landlords whose buildings can be renovated first to commit to fair rental terms and prioritize the return of pre-disaster occupants. Professionals can be aggressively involved on site, advising, supporting, and guiding but they should –as many are already doing-, work with immediate, on the ground instructions and concrete support. The economic life of the neighborhood will be equally important to reignite. Business owners were suffering, and the pandemic has not slowed down –to the contrary. Short of re-inviting them and providing them with the incentives to relocate here, many will find it easier to operate remotely. There will be a time to introduce long-term planning, reconsider the relation between the port and the city, the location of the Electricity Du Liban building and the huge footprint it occupies, the design of a memorial, and many other wonderful ideas that architect and urbanist friends have proposed.3 However, these will only be possible if we preserve what is unique about the districts. The threat of planners, surveyors, and others to freeze areas until comprehensive assessments are made and a vision is set in place will work against the interests of residents. Many don’t have the luxury of waiting and they will settle permanently elsewhere. Landlords at the brink of bankruptcy will sell their property at discounted prices to developers and realtors who have been coveting these districts before the blast. Meanwhile, property regulations and building incentives inscribed and zoning regulations and revised building laws provide unchallenged enticement for those who look to make profit by wiping out the neighborhoods. The blast would have just precipitated what was already in place. Cities are made of people. Their value is anchored in the multiple forms of inhabitance, the practices, imaginations, and interactions, individual and collective. Buildings, streets, parks, or backyards have important social values as the frames in which people dwell and engage each other. Through the accumulation of their practices, many of these spaces come to embody important heritage value: they personify memories and eventually come to reflect shared communal histories and identities, capable of bringing people together. Beirut’s soul is its people; we need to start with them. 1 In this article, I speak only of the middle-class neighborhoods surrounding the port. Karantina, Badawi, or Khandaq el Ghamik and Beirut Downtown have gone through different trends and should be the subject of another piece. 2 Figures were taken from the Beirut Building Environment Database, developed by the Beirut Urban Lab. For more, check our database here. 3 I am indebted to friends like Serge Yazigi, Omar Blaik, and Shohag Ohanissian for some of these suggestions.
